HACCP Guidelines for Processing Facilities
Food processing facilities are required to follow a number of health and safety guidelines to ensure a work environment that is safe for employees and products that are safe for human consumption. Among the many requirements and guidelines from the Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) are principles for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP), intended to aid processing facilities in preparing effective safety standards in the facility.
What is HACCP and Why Does It Matter?
HACCP is an internationally supported guide for ensuring food products are handled, produced, and manufactured in a safe manner. This tool helps food processing facilities to identify risks and food safety hazards in order to develop proactive plans for mitigating these risks.
HACCP can be broken down into two key components:
- Hazard Analysis: Identifying food safety risks such as microbiological, chemical, and physical contaminants.
- Critical Control Points: Points in food processing at which controls can be implemented to prevent or reduce possible hazards.
The proper use of an HACCP plan is vital for safety compliance in the food industry, protecting everyone from employees to consumers to top-level management.
Preparing to Implement HACCP
Before a food processing facility is ready to implement HACCP and create a plan for addressing identified hazards, it must take the proper steps to prepare. Here are five things you should do before you begin HACCP implementation:
1. Assemble a Committed Team
The first step is to form a team that will take on HACCP implementation. This can be either a combination of employees and external consultants or a solely internal team, but whatever the team looks like, it should be fully supported by top-level management to ensure success. The most effective teams should bring depth and breadth of knowledge and expertise related to the products and processes being evaluated.
2. Determine Resources and Training
The HACCP team should be properly trained in what HACCP is and their goals for implementation. They also should be appropriately equipped with the tools and resources needed to effectively complete HACCP implementation, which will vary depending on the specific facility and HACCP goals.
3. List All Product Ingredients
The HACCP team will need a highly detailed list of every ingredient used to prepare the product or products being evaluated. This list should include every raw material and information on the storage of these ingredients.
4. Outline All Processes
The entire journey each product under evaluation will take — from receipt of raw materials to final product shipment — needs to be outlined in great detail. An ideal way to do this is with a flow chart that illustrates a start-to-finish process, including each step taken.
5. Ensure Prerequisite Compliance
Proper HACCP can only be implemented with certain prerequisites. While some prerequisites are necessary for all processing facilities, others should be determined by the specific facility and evaluated before moving on to HACCP.
Some common prerequisites include:
- Using approved suppliers
- Access to safe drinking water
- Integrated pest management
- Proper stock rotation measures
- Necessary employee training
- Proper equipment maintenance
- Facility layout
- Employee hygiene
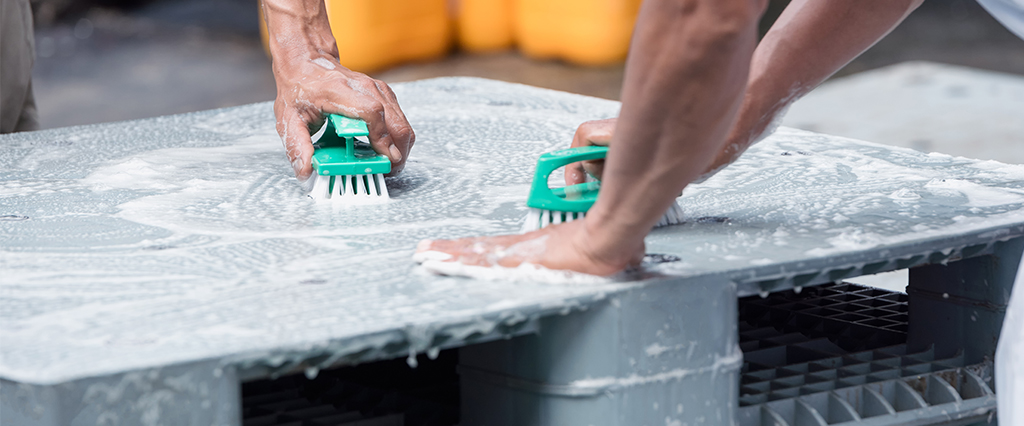
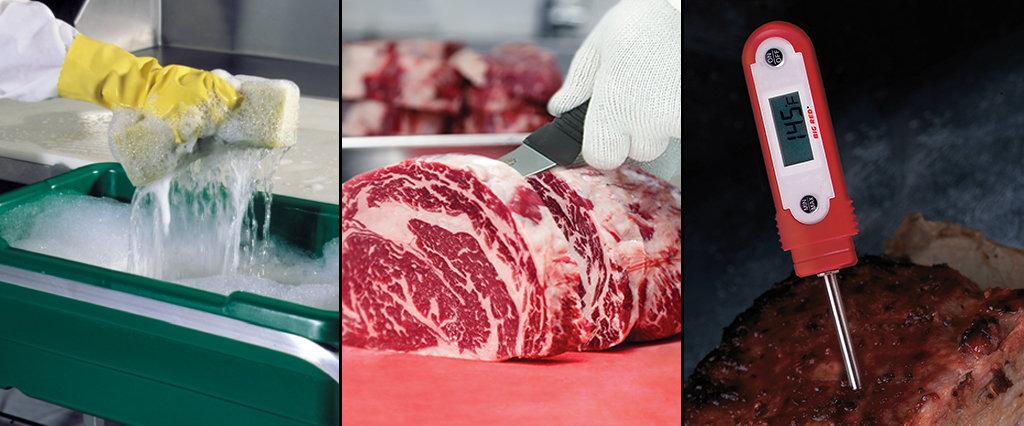
- Proper cleaning and sanitization
HACCP is intended to help identify more specific hazards and risks, so the more broadly applicable and generically identifiable hazards must be addressed beforehand.
Seven Steps for Implementing HACCP
Now that you’ve assembled a team, gathered information and resources, and ensured all prerequisites are met, it’s time to begin implementing HACCP. The HACCP team should move through these seven components of HACCP to perform the analysis and identify controls:
1. Conduct Hazard Analysis
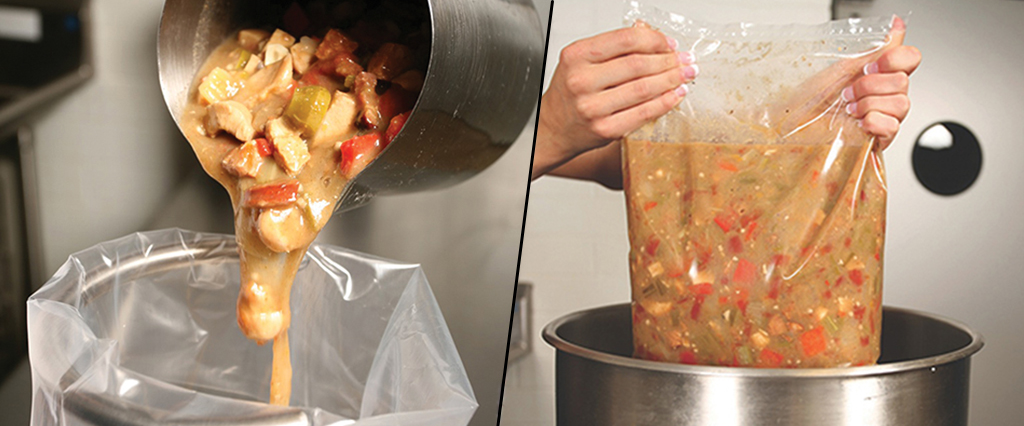
Analyze food handling processes throughout the facility for their potential to introduce contaminants or other hazards into the facility and products. These hazards should be both identified and evaluated for the level of risk they pose to food safety.
2. Identify Critical Control Points
Once hazards are identified, the HACCP team must review the surrounding process for critical control points (CCPs) at which steps can be taken to prevent or reduce the likelihood of these hazards entering the process. These CCPs could include anything from temperature checks to scanning for contaminants to adding extra sanitation measures.
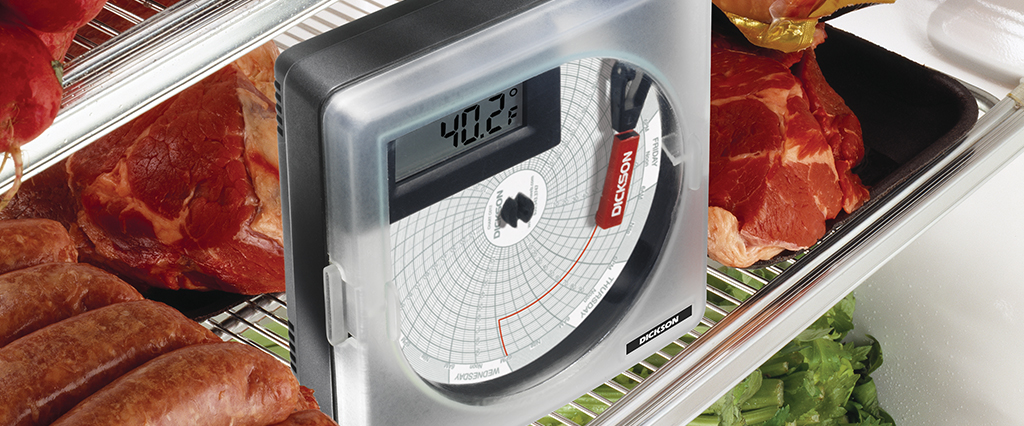
3. Establish Critical Limits
To determine whether the chosen CCPs will actually address a given hazard, they need to be given specific criteria known as “critical limits.” These limits should be measurable, such as a temperature or time. These measures should also have limits, like a minimum and maximum time or the highest and lowest allowable temperatures.
4. Set Up Monitoring Procedures
Now that CCPs have been identified and limits have been set, the team should outline procedures for monitoring these processes on an ongoing basis. This routine quality assurance, whether performed by employees or through automated systems, should record critical limits and ensure hazards are being properly mitigated.
5. Determine Corrective Actions
As CCPs are implemented and monitored, failures or deviations may crop up. In the event of such failures, you should already have a plan in place for what corrective actions will be taken. These corrective actions should identify and eliminate the failure, ensure the CCP is working properly once more, and prevent future failures. It should also include taking steps to make sure no faulty product was shipped out to consumers, recalling anything that slipped past quality assurance checks.
6. Create Verification Procedures
Beyond routine monitoring, you should also perform more in-depth verification of the effectiveness of CCPs. Verification procedures should include calibrating systems, testing operational parameters, reviewing records, and identifying large-scale changes needing HACCP evaluation.
7. Develop Record-keeping Procedures
Finally, the HACCP team should outline appropriate record-keeping procedures for ongoing recording of adherence to HACCP-identified safety measures throughout all operations. These records will be invaluable for tracing any future failures back to their source to establish proper corrective actions.
Equip Your Processing Facility for Success
From quality thermometers to personal protective equipment and sanitation tools, at Bunzl Processor Division, we have all the tools you need to effectively implement your HACCP plan and its prerequisites! Take a look at our catalog to stock up on the supplies you need for top-notch compliance.